New law requires New York museums to label Nazi-looted works
A new New York state law that requires museums to identify works of art looted during the Nazi period may affect hundreds of paintings and sculptures in famed Manhattan institutions — including MoMA and the Met.
The law, which passed last week, is part of a legislative package that seeks to combat anti-Semitism and is also requiring schools to offer courses on the the Holocaust.
Between 1933 and 1945, the Nazis engaged in the biggest plunder in history, stealing more than 600,000 art works from museums and private collectors. Although some looted works have been returned to the heirs of the original owners, most are still hanging in museums and in the homes and offices of private collectors around the world.
Efforts by family members to seek restitution by suing museums have mostly failed on legal technicalities, such as statutes of limitations, experts told The Post.
The new law, which requires museums to set up placards in front of art “which changed hands due to theft, seizure, confiscation, forced sale or other involuntary means” may do little to help the heirs get their family’s assets back. But it offers some measure of justice, according to Timothy Reif, who great-uncle’s art collection was looted by the Nazis.
“The first step towards justice is knowledge, awareness and education,” Reif, a federal judge, told The Post.
Anna Kaplan (D-Nassau), the state senator who sponsored the legislation. said that she hoped that it would “empower” the art community to be more accountable.
“When the Nazis looted over 600,000 works of art from Jewish families during the Holocaust, they did so because they were trying to erase Jewish culture, and for museums to continue trying to erase the history of what happened is unconscionable,” she said in a statement to The Post. “This new law compels museums to do the right thing and acknowledge the painful history of the Holocaust, and it’s self-policing by empowering the art community to get involved, speak out, and keep museums honest and accountable when they’re failing to do the right thing.”
Below are nine Nazi-looted works in New York City museums, according to experts.
‘The Actor’ by Pablo Picasso
Currently at The Met
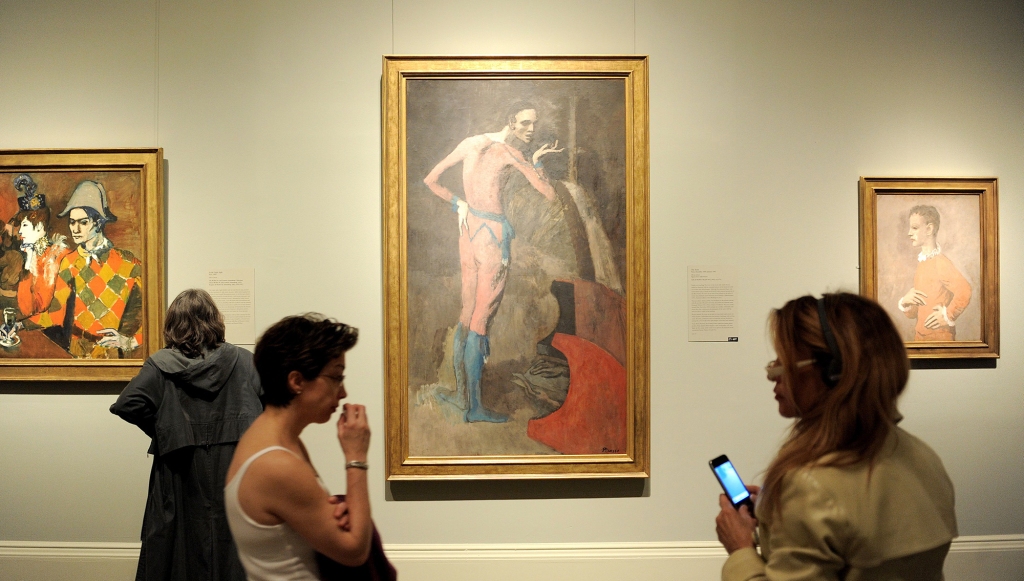
Estimated at more than $100 million, the 1905 painting was owned by Paul Leffmann, a German Jewish businessman forced to flee the Nazis in 1938. It was sold under duress for $13,200 to a Paris dealer when his family left Cologne, according to court papers.
In 1952, the Picasso was gifted to the Metropolitan Museum of Art by New York heiress Thelma Chrysler Foy, who had bought it for $22,500 from the Knoedler gallery 11 years earlier.
Leffman’s heirs sued the Met but lost an appeal in 2019 when it was ruled that they had waited too long to file their restitution claim.
“The Metropolitan Museum of Art has a long and well documented history of being transparent regarding works of art sold during the Nazi era and seeking resolution for any object that has been identified as illegally appropriated without subsequent restitution,” a spokesperson for the museum. “We have been following this legislation closely and are now reviewing its compliance components.”
‘Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer’ by Gustav Klimt
Currently at The Neue Galerie

This iconic 1907 painting of the Austrian-Jewish socialite was stolen by the Nazis along with other assets of the Bloch-Bauer family in Vienna after the annexation of Austria by the Nazis in 1938.
The fight for the portrait was documented in the 2015 Hollywood film “Woman in Gold,” starring Helen Mirren. As shown in the movie, Maria Altmann, a member of the Bloch-Bauer family, successfully reclaimed the painting through the court system. She then sold the painting to Estée Lauder heir Ronald Lauder for $135 million, and it is on permanent display at the Neue Galerie.
“The Neue Galerie has long supported efforts connected to the restitution of artworks stolen by the Nazis,” a Neue Galerie spokeswoman told The Post Friday. “The most famous work in the museum’s collection, ‘Adele Bloch-Bauer’ by Gustav Klimt, was itself a looted work, and its history is clearly displayed in our galleries and on our website.
‘Portrait of Tilla Durieux’ by Auguste Renoir
Currently at The Met
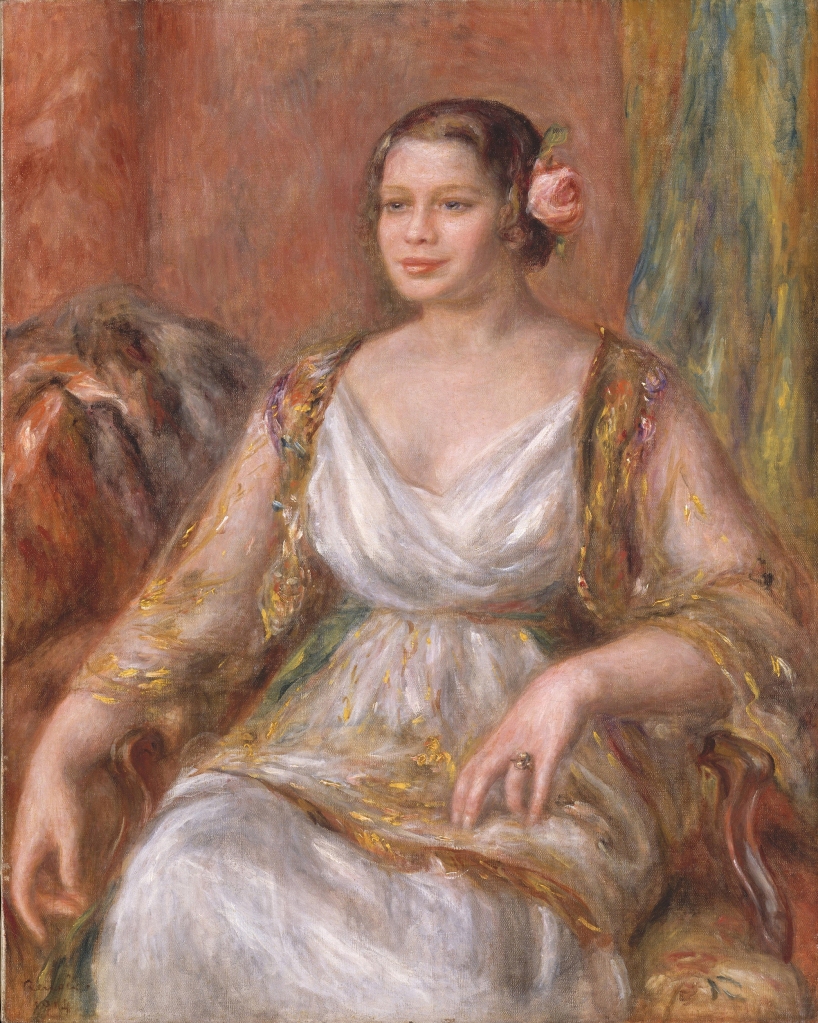

The famed Renoir was 72 when he painted this portrait of the Berlin actress in 1914 — and so stricken with arthritis that he did it with the brush strapped to his hand.
Durieux, known for her stage and screen work, took her portrait with her when she fled Nazi Germany for Yugoslavia in 1933.
Her heirs said that she sold the painting under duress two years later. The painting found its way to Paris and later to New York, where it was donated to the Met in 1960.
‘Poet Max Hermann-Neisse,’ ‘Self Portrait with Model’ and ‘Republican Automatons,’ all by George Grosz
Currently at MoMA
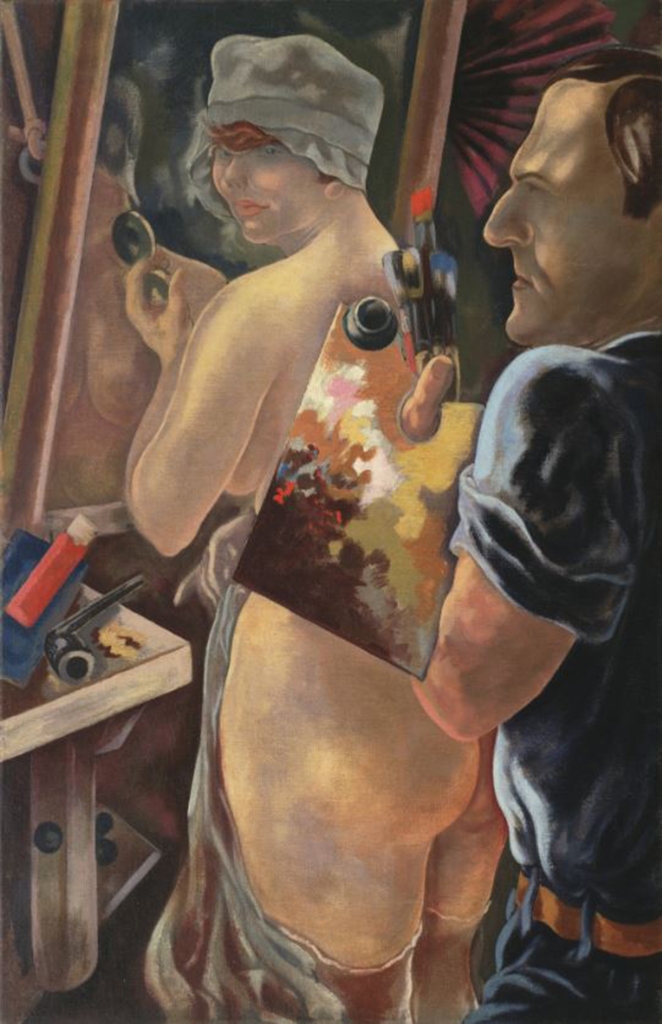



Grosz, a virulent anti-Nazi, fled Germany in 1933, accepting a teaching position with the Art Students League in New York.
His heirs tried to get these three works, dating from 1920-1928, back from the Museum of Modern Art but said the gallery played dirty: trouncing them on a legal technicality and saying the family filed their 2009 claim too late.
MoMA, which acquired the paintings between 1946 and 1954, rejected the claim that the works had been looted by the Nazis.
A spokeswoman for the MoMA told The Post this week, “We currently know of no artworks at MoMA that require action under the new law.”
‘Still Life: Job’ by Pablo Picasso
Currently at MoMA

This 1910 work was previously part of the collection of Alphonse Kann, one of France’s biggest collectors. Francis Warin, an heir, told The New York Times in 2000 that he had photographs of the Cubist work on the walls of Kann’s home outside Paris in the late 1920s.
The painting was seized, along with Kann’s other assets, when the Nazis invaded Paris in June 1940 and was later sold to a Swedish dance director in Paris.
“Still Life: Job” eventually made its way to New York and was acquired by former New York Governor Nelson Rockefeller in 1950. He donated the painting to the MoMA in 1979.
Warin reached out to MoMA but was not able to trace the provenance of the work.
‘Le Moulin de la Galette’ by Picasso
Currently at The Guggenheim
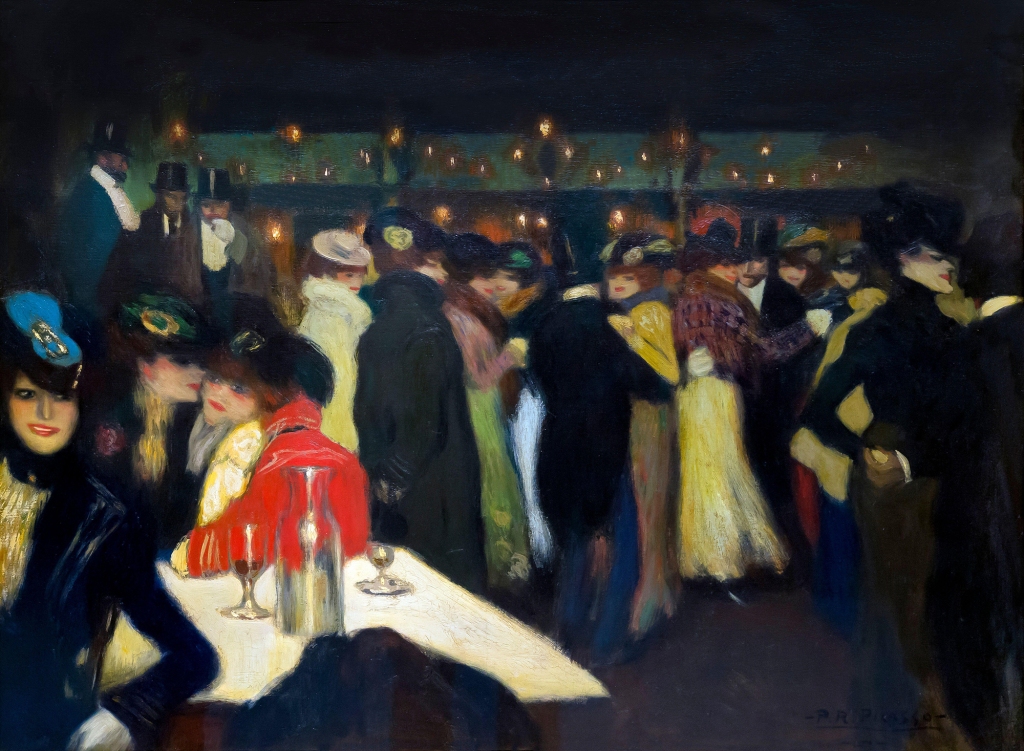

and
‘Boy Leading at Horse’ by Picasso
Currently at MoMA
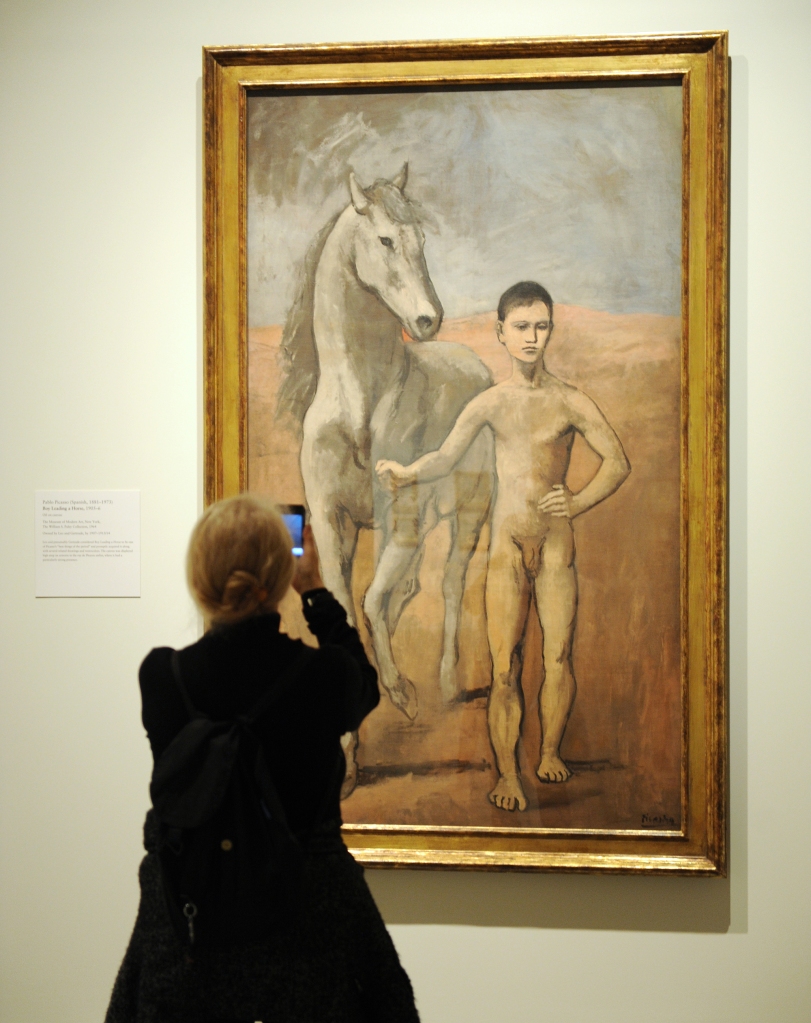

These two Picassos — dating to 1900 (“Le Moulin de la Galette”) and 1906 (“Boy Leading a Horse”) — once belonged to German-Jewish banker Paul von Mendelssohn-Bartholdy. Before his death from heart failure in 1935, he bequeathed his art collection to his wife Elsa, who was forced to sell much of the couple’s holdings under Nazi duress, according to reports.
When Julius Schoeps, a grandson of one of von Mendelssohn-Bartholdy’s sisters, tried to claim the paintings from the museums in 2007, the museums sued him to assert their claims on the works, which had been on display for dozens of years. The lawsuit was settled for an undisclosed amount two years later, and the paintings remain at the museums.
Read the full article Here


